


Next: Round-robin Policy
Up: Introduction
Previous: Policy Model
Contents
The simplest method for a policy to select replica addresses is to
always return the first 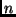 addresses from the list. This method does not
differ from what a typical DNS server does. Basically, it returns all the
site addresses it knows. The fact that it may ignore an exceeding number
of addresses (as it only returns a certain number of them, even if the list
of addresses is very long) does not change anything - it still gives
the same response each time it is queried (see Figure 4.1).
addresses from the list. This method does not
differ from what a typical DNS server does. Basically, it returns all the
site addresses it knows. The fact that it may ignore an exceeding number
of addresses (as it only returns a certain number of them, even if the list
of addresses is very long) does not change anything - it still gives
the same response each time it is queried (see Figure 4.1).
Figure 4.1:
The static policy always returns the same addresses
|
|
The reason for including this straightforward address selection method
is very simple. The main purpose of the redirector is to support
domains containing replicated services. However, these domains may also
contain machines that host non-replicated services for which
the static name-to-address mapping is good enough.
Making the redirector capable of servicing such machines as well
increases its flexibility. We will also see later in this chapter that
this policy also serves as a fallback if more advanced policies fail
to return a list of replicas.



Next: Round-robin Policy
Up: Introduction
Previous: Policy Model
Contents
root
2002-08-27
![\includegraphics[width=12cm]{xfig-static.eps}](img13.png)